Spring Security
1. 校验流程


入口在AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter,它的实现如下图所示,可以发现它的子类只有一个UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter,其中的attemptAuthencation方法就如下实现。
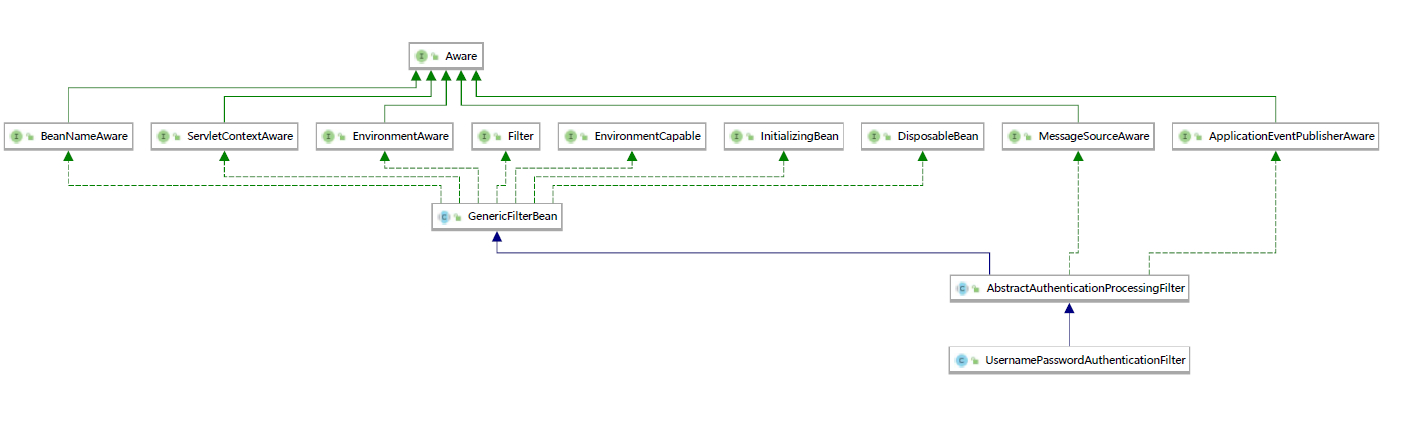

从上图可以看到尝试授权前先创造了一个Token,而username就被作为了principal也就是主体,password被作为了 credentials也就是认证证书。然后通过authenticationManager进行认证操作。Token的实现类图如下图所示。

而AuthenticationManager的类图如下,可以发现默认实现类为ProviderManager。

其中ProviderManager的授权方法如下图所示。

可以看到主要就是通过AuthenticationProvider来进行实际的授权工作,找到第一个可用的AuthenticationProvider来进行授权。
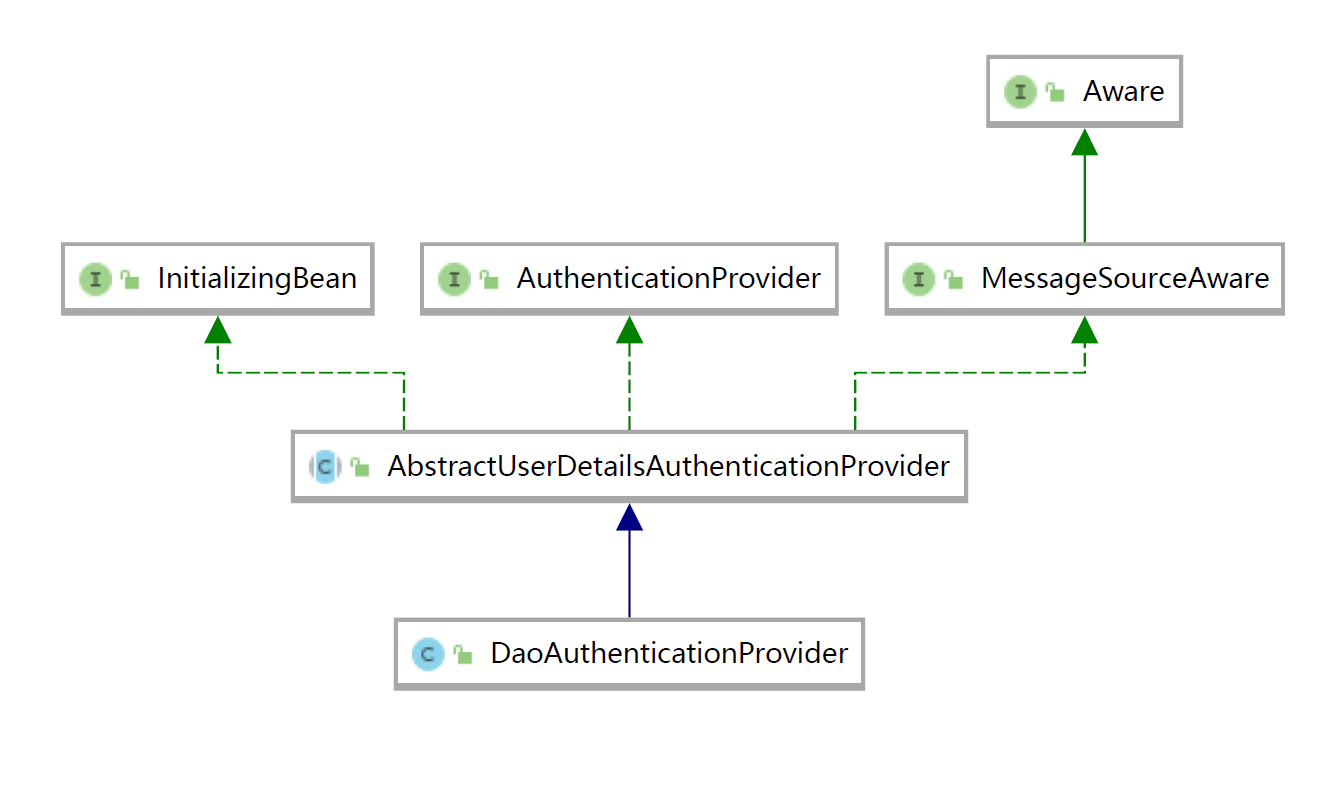
其中默认的Provider为AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider,有一个子类实现了它为DaoAuthenticationProvider。但是主要的方法就在当前抽象类中。

可以看到这里做了用户的缓存,根据Username来查询,如果没有查询到的话就会找retrieve方法获取。
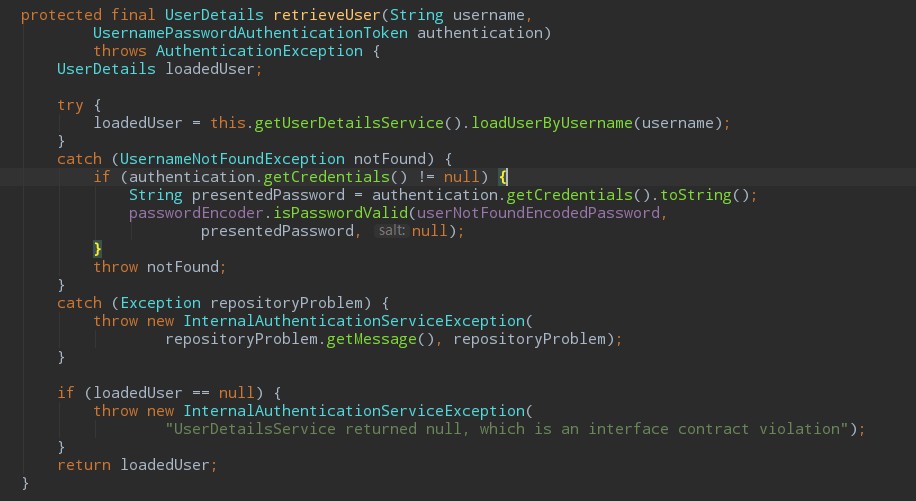
以上是获取用户的代码,可以发现是通过UserDetailsService().loadUserByUsername(username)实现的。至此就用到了我们自己实现的相关方法。
2. 架构和实现
2.1 核心组件
2.1.1 SecurityContextHolder,SecurityContext 和 Authentication对象
SecurityContextHolder是最基础的对象。它存放了当前应用上下文的细节信息。默认是通过ThreadLocal来实现的,当然实现方式可以通过配置进行更改。
获取当前用户信息
UserDetails是Spring Security的一个principal实现。可以在应用中的任何一个地方通过以下代码获取到用户的用户名称。
Object principal = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getPrincipal(); if (principal instanceof UserDetails) { String username = ((UserDetails)principal).getUsername(); } else { String username = principal.toString(); }
UserDetailsService
/**UserDetailsService通过用户名称参数来获取用户具体的UserDetails信息。 */ UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException;UserDetailsService纯粹是用户数据的DAO层(坑啊,为啥叫Service)。它并不进行其他的授权鉴权操作。
GrantedAuthority
GrantedAuthority集合可以通过Authentication的getAuthorities()方法得到。它是一种应用级的粗粒度的权限管理。
小结
- SecurityContextHolder 提供了访问SecurityContext对象的方法。
- SecurityContext 持有了Authentication对象和一些指定请求的安全信息。
- Authentication 代表了Spring Security中的principal.
- GrantedAuthority 一种对principal的粗粒度授权。
- UserDetails 提供一个Authentication对象需要的必要安全信息,从应用的DAO或其他的源来构建。
- UserDetailsService 用来通过一个基于String的用户名来创建一个UserDetails。
2.1.2 Authentication
Spring Security 鉴权的四个步骤:
- 用户名和密码组合进UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken中
- token传递进AuthenticationManager中进行校验
- AuhtenticationManger返回一个完整的Authentication实例当成功授权
- SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication()方法构建了一个SecurityContext.
import org.springframework.security.authentication.*; import org.springframework.security.core.*; import org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority; import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder; public class AuthenticationExample { private static AuthenticationManager am = new SampleAuthenticationManager(); public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); while(true) { System.out.println("Please enter your username:"); String name = in.readLine(); System.out.println("Please enter your password:"); String password = in.readLine(); try { Authentication request = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(name, password); Authentication result = am.authenticate(request); SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(result); break; } catch(AuthenticationException e) { System.out.println("Authentication failed: " + e.getMessage()); } } System.out.println("Successfully authenticated. Security context contains: " + SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication()); } } class SampleAuthenticationManager implements AuthenticationManager { static final List<GrantedAuthority> AUTHORITIES = new ArrayList<GrantedAuthority>(); static { AUTHORITIES.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_USER")); } public Authentication authenticate(Authentication auth) throws AuthenticationException { if (auth.getName().equals(auth.getCredentials())) { return new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(auth.getName(), auth.getCredentials(), AUTHORITIES); } throw new BadCredentialsException("Bad Credentials"); } }
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 3.0协议 。转载请注明出处!